By Gina Macris
If the state of Rhode Island were building a network of roads to help adults with developmental disabilities get to their jobs, town libraries, or classes at the local Y, then construction could be described as well underway.
But that’s not to say the infrastructure is complete and travelers are rushing to use these new highways on their way to richer lives.
This image of a work in progress serves, in effect, as a snapshot of what a federal court monitor sees in an ongoing transformation of the state’s developmental disability service system.
In a recent report to U.S. District Court Judge John J. McConnell, Jr., Charles Moseley says Rhode Island has made solid gains in its efforts to comply with a 2014 consent decree enforcing the Olmstead decision of the Americans with Disabilities Act, which requires disability-related services to be offered in the least restrictive setting that is therapeutically appropriate. And that setting is presumed to be the community.
The state has increased funding by $11 million, filled key leadership posts, offered more training, and put into place policies and programs to help adults with developmental disabilities find jobs and enjoy activities in their communities.
Priorities for Compliance
While acknowledging these efforts, Moseley indicated the state is still out of compliance with the consent decree. Among his top recommendations, Moseley said the state must:
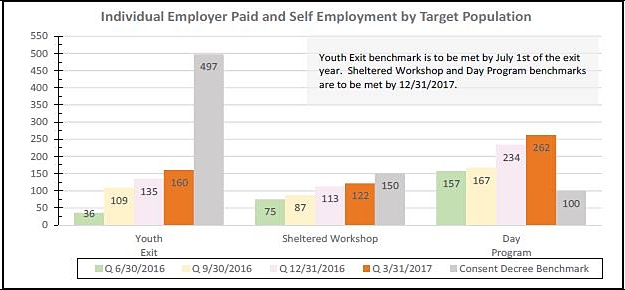
• Strengthen supported employment for young adults up to the age of 25. Job placements for young adults are “significantly below consent decree requirements,” he said.
• Increase funding to expand supported employment and community-based, integrated day services during the next fiscal year, beginning July 1, and in future budgets. The state “needs to take steps to ensure additional funding is available to address caseload increases” related to special education students moving to adult services, he said.
• Increase providers’ capacity to provide services. “Provider agencies do not yet have the numbers of trained staff needed to ensure the provision of services and supports required by the consent decree” Moseley said.
• Eliminate service delays.
Moseley says the Division of Developmental Disabilities (DDD) and the Office of Rehabilitative Services (ORS) have said that service providers can meet the need for employment and community –based supports required by the consent decree.
“But families of individuals with IDD (intellectual or developmental disabilities) who are requesting DDD services for the first time have reported to the monitor that access to needed supports has been prevented or delayed by providers who refuse to accept new referrals,” Moseley said.
“Provider refusals appear to be directly linked to DDD payment rates and rate setting practices,” he said.
Twenty-two of the state’s 36 private service providers have agreed to participate in a program of one-time bonuses paid for staff training, job placements, and job retention, according to state officials.
That initiative is still accepting applicants and cannot yet be evaluated, Moseley said, although it is expected to ease the service gap over time.
Moseley found it “important to note,” however, that the state has not offered any other kinds of incentives to agencies that chose not to apply to the incentive program, or to providers that did not receive start-up costs to convert sheltered workshops and day programsto community-based operations.
Moseley is asking the state to give him an accounting by Feb. 28 of the number of clients who were refused or faced service delays between July and December of 2016, including the names of the agencies, the reasons given, the length of any delay, and the state’s recommendations for improving access to services.
He also gave notice that he will want a similar report for the three-month period between January and March, as well as another update at the end of June to use as a guide in determining whether recent initiatives put into place by the state are having a positive impact.
State is Playing Catch-up
Moseley submitted a 48-page report to McConnell Jan. 25 in anticipation of a hearing Feb. 14 on the status of the consent decree.
The state’s positive momentum, supported by the $11-million budget increase, is all the more significant because most of it has been accomplished in the year since McConnell became personally involved in the enforcement of the consent decree in January, 2016.
After McConnell signaled he would take the bench on the case, the direct day-to-day supervision of the developmental disabilities division has shifted from the Department of Behavioral Healthcare, Developmental Disabilities and Hospitals to Jennifer Wood, Deputy Secretary of the Executive Office of Health and Human Services.
Even though Wood has put efforts to comply with the consent decree into overdrive, the state is still playing catch-up with the progressively stiffer requirements of the highly prescriptive agreement, which was marked by two years of inactivity at the outset.
The consent decree, signed April 8, 2014, has a ten-year term. At the end of 2015, seeing little progress, the U.S. Department of Justice and the court monitor asked McConnell to take the case under his wing.
During the most recent hearing, in September, 2016, the state avoided contempt proceedings for failing to hit two targets. One of them, the disbursement of raises for direct service workers, was accomplished Oct. 1. The other was the lag in employment of young adults – a problem that has only grown bigger. At the same time, McConnell said he relied on Moseley to hold the defendant’s “feet to the fire.”
Moseley Wants More Information
Even at the September hearing, Moseley was digging deeper. He pressed the state to better identify young adults and high school special education students who should be counted as members of the consent decree population and enjoy protections designed to prevent them from living lives of isolation.
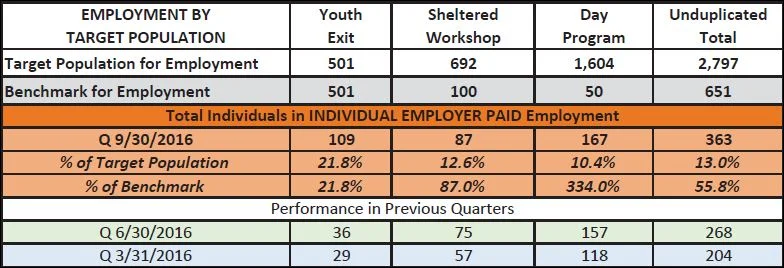
Moseley’s report relies on data available as of Oct. 31, but he says the state subsequently informed him that the count of young adults who left school since the 2013-2014 academic year has increased by 350, from 151 to 501.
The report says 29 of these young adults have received job placements, a number that is more than six months old. The consent decree required “all” members of this group to have at least part-time jobs by July 1, 2016.
The monitor continues to press DDD, ORS, and the Rhode Island Department of Education (RIDE) for more detailed information on several areas of implementation where he sees the state lagging.
By Feb. 28, Moseley wants reports on:
Staff Training
• a plan outlining how DDD and ORS will provide the monitor regular updates on appropriate training for direct service workers at various agencies who provide daytime services. The current number of trained staff statewide, 396, is too low, he says.
Average Hours Worked
• a plan and strategy for increasing the average number of hours per week worked by individuals in supported employment. The current weekly average, 8.6 hours, falls far below the average 20 hours specified in the consent decree. Implementation of the plan should begin March 1, Moseley says.
Career Development Plans
• an umbrella “operational plan” for 1) expanding critically-needed training for professionals and families on career development, 2) ensuring more than 3,000 individuals protected by the consent decree have high quality career development plans by June 30, and 3) making provisions for regular updates to the monitor on this topic beginning April 1. Currently, 774 individuals have career development plans, according to Moseley’s data. These plans are intended not only to describe individualized long-term goals, but to include strategies and a sequence of real-life activities for helping individuals work toward those targets. Moseley said there are signs such details are lacking from many existing career development plans.
High School Internships
• data from RIDE and ORS showing the number of high school special education students who participate in at least two trial work experiences, each lasting a minimum of 60 days. RIDE has indicated it is keeping track of these numbers but has yet to provide the monitor with the information, Moseley says.
• data from DDD showing implementation of a so-called “transition timeline”, including notifications to families and other activities involving special education students in high school that prepare them for adult living.
Benefits Counseling
• a report from DDD on how it will ensure individuals deciding on jobs receive counseling about the way their earned income might affect the government assistance they receive, as well as evidence that the counseling is covering the required information. The monitor found that only 65 people had benefits counseling last June 30, the latest date for which statistics were available.
Moseley also noted that the state has developed a process for individuals to seek a variance if they want to opt out of employment, but no one has applied for one. He said he have more to say about the variance process by the end of the month but wants recommendations from the state by March 31 on ways to improve the variance process.
Employment First Task Force
Moseley addressed the future of the Employment First Task Force, saying it “has the potential to provide an independent and meaningful role in supporting the ability of the State to accomplish the reforms identified by the consent decree."
“But change needs to take place if the task force is to achieve its full potential,” he said.
The consent decree intends the task force as a bridge between the community and the government, or as Moseley put it, “an independent, voluntary group of advocates and stakeholders who are not directly involved in state agency operations.”
While the consent decree says the group should make policy recommendations, it doesn’t say what areas the task force should research, or to whom it should make its recommendations, said Moseley. He also noted that it has no administrative staff or oversight from any state agency.
Moseley said he wants some changes in the task force “without compromising the separate and independent voice of advocates and stakeholders.”
Ultimately, he wants the task force to make annual reports for the monitor, the state, and the public on barriers to implementing the consent decree and ways to overcome them.
Moseley called on EOHHS to give the task force some staff support. And he asked Kevin Nerney, the task force chairman, and Jennifer Wood, the Deputy Secretary of EOHHS, to convene a small work group to map out the respective roles and responsibilities of the state and task force members and to report back to him by Feb. 28.
Click here to read the entire monitor's report.